Are you a Linux user who wants to know how to run files? Don’t worry, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’ll be discussing the various methods of running files in Linux so you can use them to their fullest potential. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced Linux user, you’ll find the information here useful. We’ll go into detail about running executable files, shell scripts, and more! So keep reading to find out how to run files in Linux!
Open the Terminal – The first step to running files in Linux is to open the Terminal application
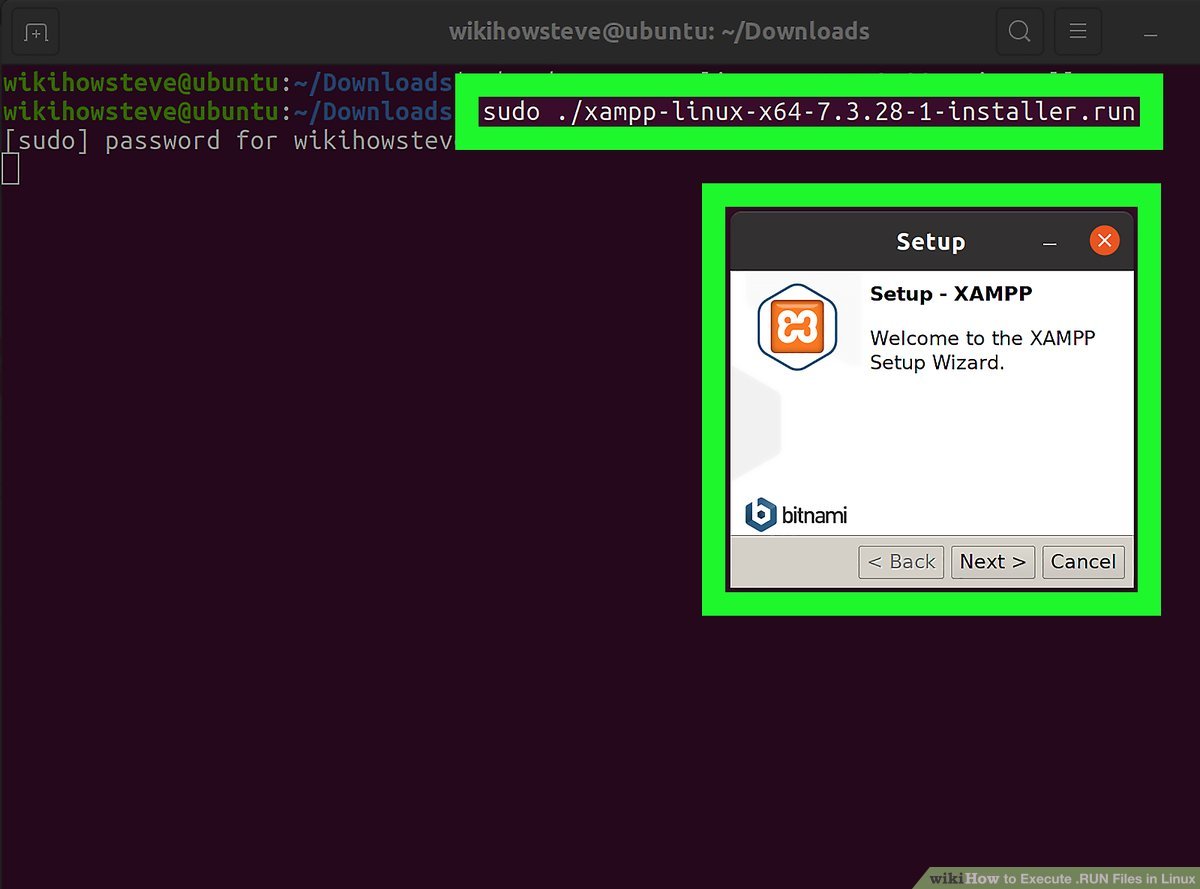
The Terminal is a powerful tool in Linux, and the first step to running files is to open it. To do so, simply search for ‘Terminal’ in your applications menu, or press CTRL+ALT+T to open the Terminal window. This opens up a world of possibilities, allowing users to run commands and scripts to get the most out of their Linux system.
To open the Terminal, press the Ctrl + Alt + T keys simultaneously.
Opening the Linux Terminal is a simple process; simply press the Ctrl + Alt + T keys at the same time to launch the program. This convenient shortcut allows users to quickly access the Terminal and run commands on their Linux system.
Navigate to the File Location – Once the Terminal application is opened, use the cd command to navigate to the folder location of the file you want to run.
If you are looking to run a file in Linux, the first step is to navigate to the folder location of the file you want to run. You can do this easily through the Terminal application using the cd command. Make sure you have the correct path for the file, so you can access and run it with ease.
Check the File Permissions – Once you’ve located the file, you need to check that you have the correct permissions to run it
Checking your file permissions is an important step when running any file in Linux, as it ensures your file will run safely and securely. Without the correct permissions, the file may not run at all, or could cause potential damage to your system. To make sure your system is secure and your file runs correctly, check your file permissions before executing the file.
To do this, use the ls -l command to list the file’s permissions.
To find out what permissions a specific file has on a Linux system, use the ls -l command to list the file’s permissions and ensure that you have permission to run the file.
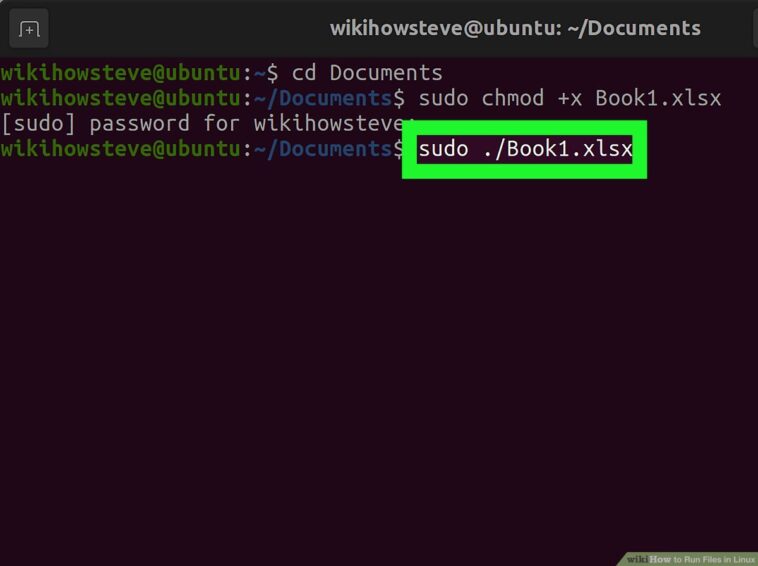
Change the File Permissions – If you don’t have the correct permissions to run the file, use the chmod command to change the file’s permissions.
Using the chmod command, you can customize the permissions of a file to ensure you have the necessary access rights to run it. This is an essential step for any Linux user to prevent any unauthorized access and ensure a secure system.
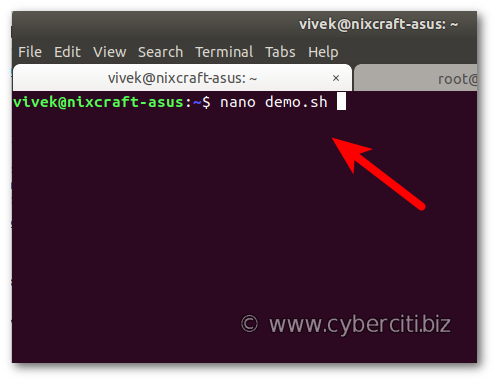
Run the File – Once you have the correct permissions, you can run the file by entering the following command: ./filename
To run a file on Linux, first ensure that you have the correct permissions, then enter the command “./filename” and hit enter. This command allows you to execute the desired file on Linux, providing you with the ability to access and use the contents of the file.
Check the Output – Once the file is run, you can check the output by using the echo command
Checking the output after running a file in Linux is easy with the echo command. After entering the command, you can see the output of the file you ran, allowing you to verify that it ran as expected. The echo command is a great tool for troubleshooting and verifying that your commands are running properly in Linux.
This command will display the output of the file.
Running files in Linux is an efficient way to manage and execute tasks. The command ‘cat’ is used to display the output of a file, providing a quick way to view the contents of a file without having to open it in an editor. This command is particularly useful for quickly checking the contents of a script before running it.
Exit the Terminal – Finally, when you are finished running the file, you can exit the Terminal application by using the exit

When you have completed the task of running a file in the Linux Terminal, it is important to exit the application properly. To do this, simply type in the command “exit” to properly close the Terminal and make sure that all processes have been properly terminated. This step is essential to ensure that no data is lost or corrupted.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings