5G – the fifth generation of the cellular, the fastest cellular network ever. But is there really a difference? In this article, we checked what differences between 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G are.
1G the first generation of the cellular network
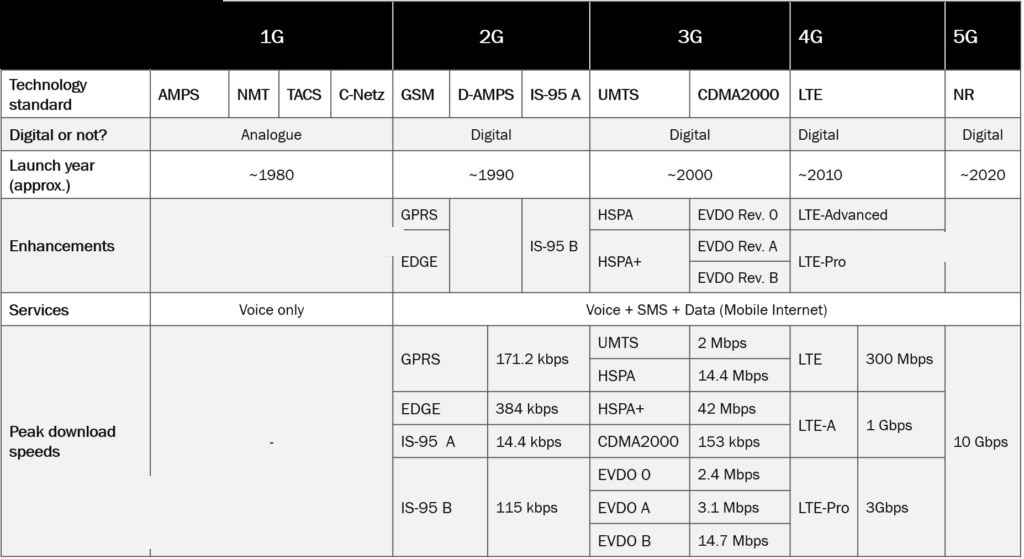
The G in the 1G stands for generation, and the 1G is basically the first generation of the cellular network. The goal of this network was phone calls on the go (wirelessly). 1G networks started in the 1980s and were offered in different parts of the world through various analog technologies. The technologies included AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System), NMT (Nordisk MobilTelefoni or Nordic Mobile Telephone), TACS (Total Access Communications System), and C-Netz (Funktelefonnetz-C or Radio Telephone Network C).
2G the second generation of the cellular network
The 2G replaced the 1G and it’s the second generation of the cellular network. 2G networks let make better quality voice calls as well as the option of text messages. 2G networks started in the 1990s and were deployed in different parts of the world through various digital technologies. The most widely used technology standard for the second generation of mobile networks is ‘Global System for Mobile Communications’ (GSM) The 2G offered two new access technologies; TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) and CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access).

3G the third generation of the cellular network
The 3G is a more similar network to the 4G network we use today (in the most west world). And it’s still be used in developed countries, and even in counties like the US in remote areas that are not inhabited. The advent of a 3G network with more data, video calling, and mobile internet began in 1998. What we may now consider a “slow” network in many large municipalities was the height of technology until 4G came along. 3G networks reach 2mbps on stationary or non-moving devices and 384kbps on devices in moving vehicles.
4G – the fourth generation of the cellular network
The 4G is today standard in most countries as well as in the United States, it was released in the late 2000s and is 500 times faster than 3G. It has been able to support high-definition mobile TV, video conferencing, and much more. When a device is moving, as when you are walking with your phone or are in a car, the top speed can be 10s of Mbps, and when the device is stationary, it can be 100s of Mbps. The 20MHz bandwidth sector has a peak capacity of 400Mbps. However, since users are sharing available sector capacity among others, observable speed experiences by users are typically in 10s -100s of Mbps.
As more people get access to mobile devices and the Internet of Things expands, as many as 24 billion devices are expected to need cellular network support by 2024. That’s where 5G comes in.
5G – the fifth generation of the cellular network
5G is the fifth generation of cellular technology. It all started with 1G networks in 1980 followed by 2G networks, which that came with additional features including SMS. Later, 3G and now 4G have been in use, which offers a smooth and fast service for our devices for different applications and browsing. for more information about the 5G network click here.


GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings