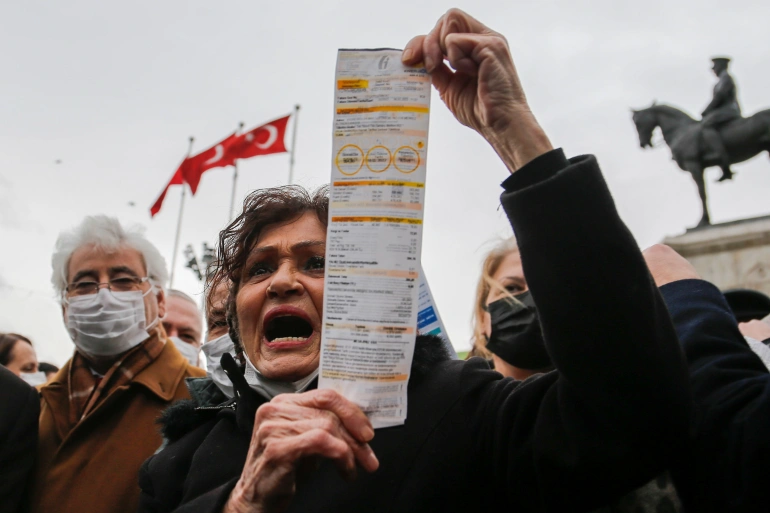
Inflation is a general increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy over time. It is usually measured as an annual percentage change. Inflation can have different causes, such as an increase in the money supply or a decrease in the productivity of workers. When inflation is high, it can be difficult for people to keep up with the rising prices.
What is inflation?
Inflation is a general increase in prices and a fall in the purchasing power of money. The main causes of inflation are either excess money supply or excess aggregate demand (or both). When the government prints more money, it reduces the value of money already in circulation. This is because there are more dollars chasing the same number of goods and services. As a result, prices go up.

Similarly, when there is too much aggregate demand (demand from all consumers), businesses will respond by raising their prices. This is because they can sell their goods at a higher price when there is more demand.
Inflation can be good or bad for an economy. It depends on the type of inflation and the current economic conditions. For example, low inflation can help boost economic growth, but high inflation can lead to economic stagnation.
How does inflation happen?
An increase in the money supply causes inflation. When there is more money chasing the same amount of goods, prices go up. Inflation can also be caused by a decrease in the production of goods, which drives up prices.

What are the different types of inflation?
There are four main types of inflation: demand-pull, cost-push, built-in, and imported.
Demand-pull inflation occurs when there is an increase in demand for goods and services in an economy. This can lead to higher prices for these goods and services. Cost-push inflation occurs when there is an increase in the cost of production for goods and services. This can lead to higher prices for these goods and services. Built-in inflation refers to expectations of future price increases. This type of inflation can lead to higher prices even if there is no increase in demand or cost. Imported inflation occurs when there is an increase in the price of imported goods and services. This can lead to higher prices for domestic goods and services.

The effects of inflation
Inflation can have a number of different effects on the economy. It can lead to higher interest rates, which can in turn lead to higher borrowing costs and slower economic growth. It can also lead to higher prices for goods and services, which can reduce consumers’ purchasing power.
Inflation can be beneficial to some groups in society, such as borrowers and savers, but it can be detrimental to others, such as those on fixed incomes. It’s important to understand how inflation works so that you can make the most of its benefits and minimize its drawbacks.
How to measure inflation
Inflation can be measured in a number of ways, but the most common method is to track the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI measures the prices of a basket of goods and services that are commonly purchased by households, and it is released on a monthly basis by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.

There are other ways to measure inflation as well, such as the Producer Price Index (PPI) and the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) deflator. The PPI measures the prices of goods and services at the producer level, while the PCE deflator measures inflation for all final goods and services purchased by households.
So, how does the CPI measure inflation? The CPI tracks changes in the prices of a fixed basket of goods and services over time. The basket includes items such as food, housing, apparel, transportation, medical care, recreation, education, and communication.
The CPI is calculated by taking the weighted average of the prices of these items. The weights are based on how much of each item is typically purchased by households. For example, housing is given a weight of 42%, which means that it accounts for 42% of the CPI basket.

Causes of inflation
A variety of factors cause inflation, but the most common cause is an increase in the money supply. When there is more money chasing after goods and services, prices go up. Other causes of inflation include:

-demand-pull inflation: This occurs when there is too much demand for goods and services in the economy. This can be caused by things like population growth or government spending.
-cost-push inflation occurs when costs go up, such as the cost of raw materials or energy. This can put pressure on companies to raise prices.
-asset inflation: This occurs when prices go up for assets such as property or stocks. This can lead to speculation and further price increases.
Conclusion
Inflation can be a confusing concept, but it’s important to understand what it is and how it can impact your life. We hope that this article has helped you to better understand inflation and how it works. While inflation can be worrisome, there are ways to protect yourself from its effects. By saving regularly and investing in assets that tend to do well in periods of high inflation, you can help safeguard your finances against the negative effects of inflation.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings